Randomized Block Design: An Introduction
Table Of Content
Four of them used mutant or genetically modified, the rest used wild-type rats. Twenty two of them involved experimental pathology, nineteen behaviour, seven physiology, one immunology and one pharmacology. Again, it was only the quality of the experimental design which was assessed, not the biological validity of results. Most papers involved several experiments, but the designs were usually similar.
Functional models for block-treatment interactions: Testing known forms of interaction
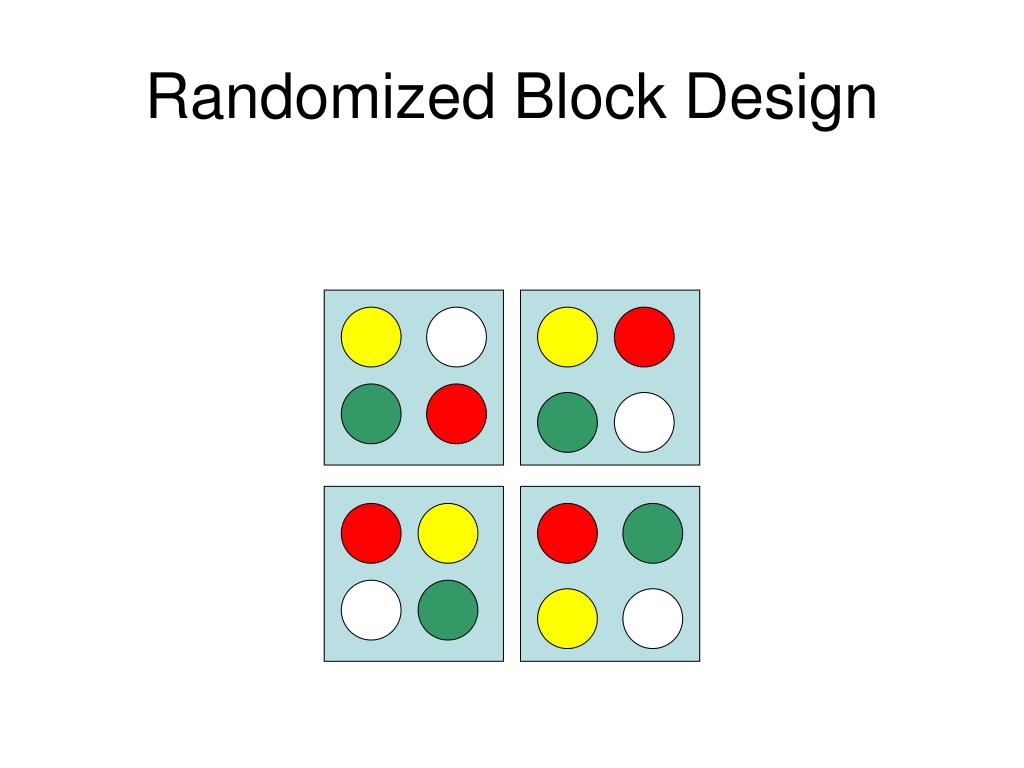
The RB design, is already widely used in studies involving pre-weaned mice and rats11. So each is regarded as a “block” and one of the treatments, chosen at random, is assigned to each pup within the litter. To improve the precision of treatment comparisons, we can reduce variability among the experimental units. We can group experimental units into blocks so that each block contains relatively homogeneous units. Randomized block design requires that the blocking variable be known and measured before randomization, something that can be impractical or impossible especially when the blocking variable is hard to measure or control. The objective is to make the study groups comparable by eliminating an alternative explanation of the outcome (i.e. the effect of unequally distributing the blocking variable), therefore reducing bias.
Statistical analysis
Too many pre-clinical experiments are giving results which cannot be reproduced. In “Completely randomized” (CR) and “Randomised block” (RB) experimental designs, both the assignment of treatments to experimental subjects and the order in which the experiment is done, are randomly determined. These designs have been used successfully in agricultural and industrial research and in clinical trials for nearly a century without excessive levels of irreproducibility. They must also be used in pre-clinical research if the excessive level of irreproducibility is to be eliminated. A survey of 100 papers involving mice and rats was used to determine whether scientists had used the CR or RB designs.
Blocked Randomization with Randomly Selected Block Sizes
This leads to a waste of scientific resources with excessive numbers of laboratory animals being subjected to pain and distress3. There is a considerable body of literature on its possible causes4,5,6,7, but failure by scientists to use named experimental designs described in textbooks needs further discussion. In the greenhouse experiment discussed in Chapter 1, there was a single factor (fertilizer) with 4 levels (i.e. 4 treatments), six replications, and a total of 24 experimental units (each unit a potted plant). Suppose the image below is the Greenhouse Floor plan and bench that was used for the experiment (as viewed from above). Non-replicated experiments are used by knowledgeable experimentalists when replications have prohibitive costs.
Statistical analysis of surface roughness during high speed edge trimming of flax-fiber composite based on the Split ... - ScienceDirect.com
Statistical analysis of surface roughness during high speed edge trimming of flax-fiber composite based on the Split ....
Posted: Sun, 25 Jul 2021 06:14:29 GMT [source]
However, when treatment assignment is open and sample size is small than a block randomization procedure with randomly chosen block sizes may help maintain balance of treatment assignment and reduce the potential for selection bias. The number of participants assigned to each treatment group will be equal when all the blocks are the same size and the overall study sample size is a multiple of the block size. Furthermore, in the case of unequal block sizes, balance is guaranteed if all treatment assignments are made within the final block [1]. However, when random block sizes are used in a multi-site study, the sample size may vary by site but on average will be similar.
Note that repeat blocks may occur when the total sample size is greater than the block size times the number of possible orderings. Furthermore, the block size must be divisible by the number of study groups. The RB design often provides better control of both inter-individual and environmental variation. Subjects within a block can be matched and each block has a small environmental footprint, compared with the CR design.
Randomized Block Design: An Introduction
Use of research electronic data capture (REDCap) in a COVID-19 randomized controlled trial: a practical example ... - BMC Medical Research Methodology
Use of research electronic data capture (REDCap) in a COVID-19 randomized controlled trial: a practical example ....
Posted: Sat, 21 Aug 2021 07:00:00 GMT [source]
All were assessed and re-assessed, blind to the previous scores, after an interval of approximately 2 weeks. The results in seventeen of the papers were discordant so they were reassessed. Each paper was searched for the words “random”, “experiment”, “statistical”, “matched” and other words necessary to understand how the experiments had been designed. The discipline and type of animals which had been used (wild-type, mutant, or genetically modified) was also noted. The aim was to assess the design of the experiments, not the quality of research. To avoid bias, cages receiving different treatments must be intermingled (see Fig. 1A,B), and results should be assessed “blind” and in random order.
When group equality requires blocking on a large number of variables:
Santana-Sosa et al. set to study the effect of a 12-week physical training program on the ability to perform daily activities in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants after they understood the concept of this research. The study was performed in accordance with the regulations and guidelines of Helsinki Declarations. At the end of the surgery, the inhalational anesthetic was turned off and the muscle relaxant was reversed using a combination of neostigmine 0.05 mg/kg and atropine 0.01 mg/kg. General anesthesia was induced 30 min after the block using fentanyl (1.5 ug/kg iv), propofol (2 mg/kg iv) and atracurium (0.5 mg/kg iv), and maintained after orotracheal intubation as balanced anesthesia using isoflurane ( 1 MAC).
Starting from the supraclavicular brachial plexus, the transducer was slid in a cephalic direction to show the transverse process of the C7 vertebra. Then, it was moved further cephalic to display the transverse process of C6, along with its characteristic anterior and posterior tubercles. The transducer was then slid posteriorly to show the posterior tubercle of C6, along with the posterior neck muscles above it (trapezius, levator scapula, and erector spinae) (Fig. 2A and B). After prepping and draping the patient using aseptic technique, the needle was inserted (in plane technique from posterior) until it reached the posterior tubercle of C6. The patient's ability to detect pinprick sensation was assessed every 5 min for 30 min following the block.
In the RB design, the experiment is split up into a number of independent “blocks” each of which has a single subject assigned at random to each treatment. When there are only two treatments, this is known as a “matched pairs” design. A two-way analysis of variance without interaction is used to analyse the results. A disadvantage of block randomization is that the allocation of participants may be predictable and result in selection bias when the study groups are unmasked. That is, the treatment assignment that has so far occurred least often in the block likely will be the next chosen [4]. Selection bias may be reduced by using random block sizes and keeping the investigator blind to the size of each block.
This randomized prospective clinical study was conducted on 58 patients scheduled for anterior cervical spine surgery under general anesthesia from November 1st, 2022, to December 2023. Patients of both sexes, aged 21 to 60 years old, with American Society of Anesthesiologist Physical Status (ASA PS) I and II, and a body mass index (BMI) from 25 to 35 kg/m2 were included in the study. It is still controversial, if the prevertebral fascia is an effective barrier for injected local anesthetics. In this case the intermediate cervical plexus block would be a phrenic nerve sparing technique [11, 21]. Reducing pain and preventing chronic shoulder pain following cervical spine decompression surgery are necessary to improve functional outcomes [20].
The needle tip was placed under the sternocleidomastoid muscle and below the superficial fascia, and then 15 ml of 0.25% bupivacaine was injected (Fig. 1C). The spread of the local anesthetic was visualized using ultrasound guidance. We need to be able to randomly assign each of the treatment levels to 6 potted plants.
Tukey's test is valid when Mandel's multiplicative model holds and when the errors independently follow a normal distribution. Unfortunately, most authors appear to use the in-valid “Randomisation to treatment group” (RTTG) design, shown in Fig. In this design, subjects are randomly assigned to physical treatment groups but the order in which the experiment is done is not randomised. This is not valid because each treatment group will occupy a different micro-environment, the effects of which may be mistaken for treatment effects, leading to bias and irreproduciblity. The purpose of randomization is to achieve balance with respect to known and unknown risk factors in the allocation of participants to treatment arms in a study [1,2].
Comments
Post a Comment